Comparison between cart-based ultrasound and portable ultrasound
When it comes to ultrasound imaging, two commonly used options are cart-based ultrasound and portable ultrasound. Both systems have their own advantages and considerations, making them suitable for different clinical settings and applications. Let's explore the comparison between cart-based ultrasound and portable ultrasound:
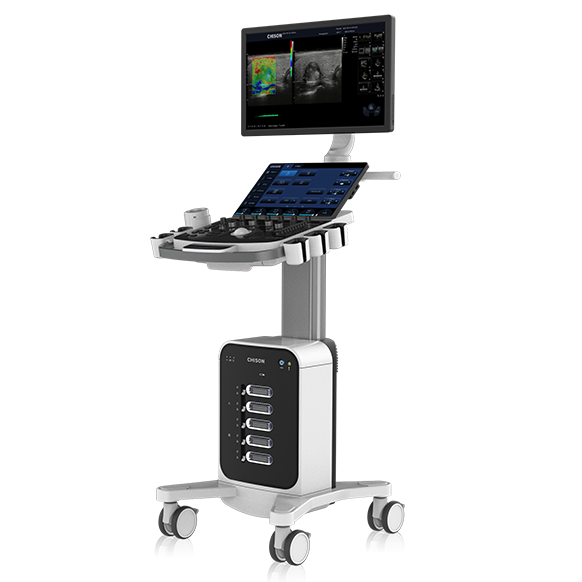
1. System Size and Portability:
Cart-based Ultrasound: Cart-based ultrasound systems are larger and require a dedicated cart or stand for operation. They are designed to remain stationary in a specific location, such as an imaging department or clinic. The size and weight of cart-based systems make them less portable compared to their portable counterparts.
Portable Ultrasound: Portable ultrasound systems are compact and lightweight, designed for easy mobility. They are handheld or laptop-sized devices that can be easily transported from one location to another. This portability allows for point-of-care imaging, bedside examinations, and use in remote or emergency settings.
2. Image Quality and Performance:
Cart-based Ultrasound: Cart-based systems typically offer advanced imaging capabilities and higher image quality. They are equipped with advanced transducers, sophisticated image processing, and more extensive features. Cart-based ultrasound systems provide better imaging performance, making them suitable for complex diagnostic procedures and detailed evaluations.
Portable Ultrasound: Portable systems have made significant advancements in image quality over the years. While they may not offer the same level of image quality as cart-based systems, they still provide sufficient imaging capabilities for many clinical applications. Portable ultrasound systems are ideal for quick evaluations, screening, and triage purposes.
3. Applications and Specialties:
Cart-based Ultrasound: Cart-based ultrasound systems are versatile and suitable for a wide range of applications across various medical specialties. They provide specialized imaging modes and features tailored to specific clinical needs. Cart-based systems are commonly used in radiology departments, hospitals, and specialized clinics where comprehensive imaging capabilities are required.
Portable Ultrasound: Portable ultrasound systems are well-suited for point-of-care settings, emergency medicine, and critical care situations. They are particularly useful for bedside examinations, quick assessments, and interventions in various clinical settings. Portable systems are commonly used in emergency departments, ambulances, primary care clinics, and remote or resource-limited areas.
4. Transducer Options:
Cart-based Ultrasound: Cart-based systems offer a wide range of transducer options, allowing for the use of specialized transducers for different imaging needs. These systems often have dedicated transducers for specific applications such as cardiac imaging, musculoskeletal imaging, or obstetrics. The availability of a variety of transducers enhances the versatility and diagnostic capabilities of cart-based ultrasound.
Portable Ultrasound: Portable systems also provide a range of transducer options, but the selection may be more limited compared to cart-based systems. However, portable ultrasound manufacturers are continually expanding their transducer offerings to cater to a broader range of applications. Portable systems typically have transducers suitable for general imaging and some specialized applications.
5. User Interface and Controls:
Cart-based Ultrasound: Cart-based systems often feature a larger display screen, comprehensive user interface, and physical control panel. The user interface allows for in-depth manipulation of imaging settings, measurements, and image optimization. The physical control panel provides tactile feedback and ease of use for the operator.
Portable Ultrasound: Portable systems have smaller display screens and simplified user interfaces due to their compact size. They may have touchscreen displays or limited physical buttons for control. While portable systems may not offer the same level of control and customization as cart-based systems, they are designed to provide intuitive and straightforward operation for quick examinations.
6. Cost Considerations:
Cart-based Ultrasound: Cart-based ultrasound systems generally have a higher upfront cost due to their advanced features, higher image quality, and specialized capabilities. Additionally, these systems may require additional costs for installation, dedicated space, and maintenance.
Portable Ultrasound: Portable ultrasound systems are typically more cost-effective compared to cart-based systems. They have a lower initial investment cost and lower maintenance requirements. Portable systems offer a cost-efficient solution for point-of-care settings and facilities with budget constraints.
7. Training and Expertise:
Cart-based Ultrasound: Cart-based systems often require more extensive training and expertise to operate effectively. The advanced features and comprehensive imaging capabilities of cart-based systems necessitate specialized training in specific applications and modalities. Proper training is crucial to optimize image quality, perform complex procedures, and interpret the results accurately.
Portable Ultrasound: Portable systems are designed for ease of use and can be operated by healthcare professionals with basic ultrasound training. They are suitable for quick evaluations and straightforward imaging tasks. Portable systems may require less training and expertise compared to cart-based systems, making them more accessible for healthcare providers in various settings.
In summary, cart-based ultrasound and portable ultrasound offer distinct advantages and considerations. Cart-based systems provide higher image quality, advanced features, and versatility for comprehensive imaging across various specialties. Portable systems, on the other hand, offer mobility, point-of-care capabilities, and cost-effectiveness for quick assessments and remote settings. The choice between the two depends on the specific clinical requirements, imaging needs, portability preferences, and budget considerations of the healthcare facility or practitioner.

